Calculated field in Dataverse are pretty cool ways to auto-magically perform calculations on any table. You can use them to automate manual calculations your users would otherwise need to make. It’s a beautiful example of leveraging the tech stack to automate manual work for your end users, which helps increase user adoption and overall happiness. 🙂
Supported Column Types
Not all columns (fields) support the creation of calculated fields. The column types that support calculations are:
- Text
- Choice
- Yes/No
- Whole Number
- Decimal umber
- Currency
- Date and Time
Calculated Field Example
Let’s walk through a business scenario to understand a possible use case for calculated field.
The team has requested to add an new field to the Opportunity table called Activity Due Date. It should automatically be set based on the following criteria:
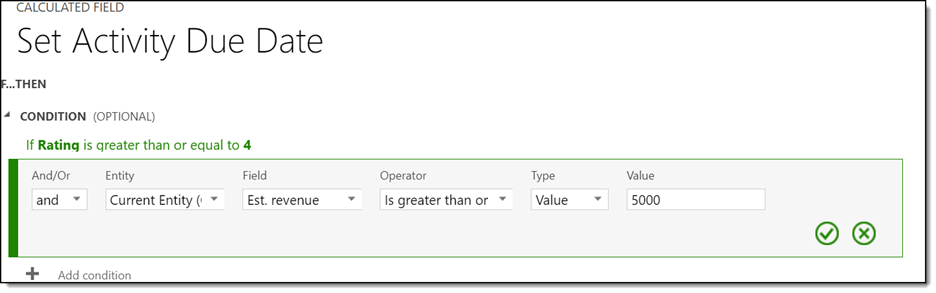
If an Opportunity is rated 4 or 5 stars, AND estimated revenue is greater than or equal to $5,000, we want to set an activity due date in 7 days.
Otherwise, the activity due date should be in 1 month.
View the Field in Action
How to Create a Calculated Field
- In Dataverse, in a solution file, add the table (in this example, the Opportunity table).
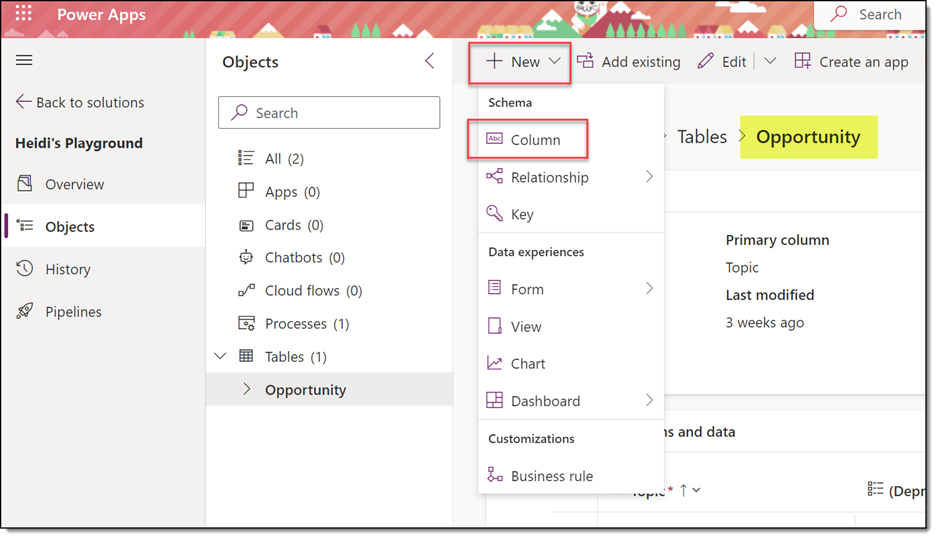
- Add a new column called Activity Due Date as a Date field. Make sure to set Behavior to Calculated! Click Save at the bottom. This will open a new window to set your calculation.
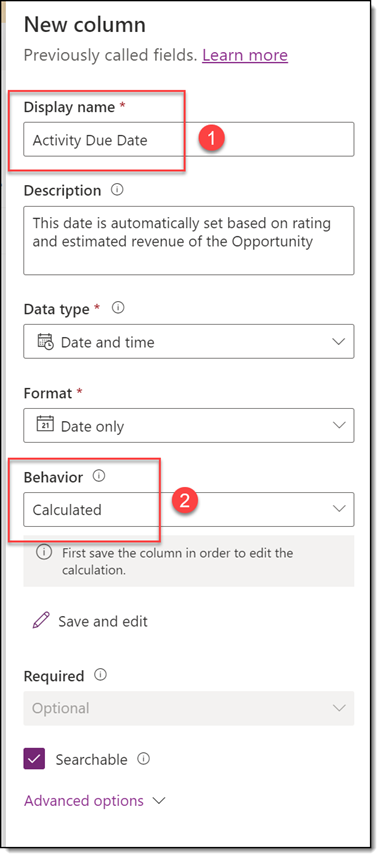
- In the Calculated Field window that opened, create your calculation. In the Condition section, we will add the following criteria.
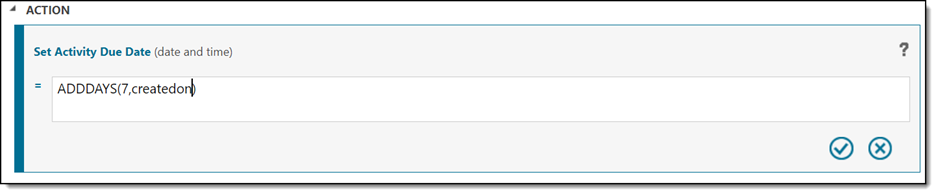
- In the Action section, we will add the following calculation, to add 7 days past the created on date:
- Next, click + Add Else at the bottom of the calculated field builder:
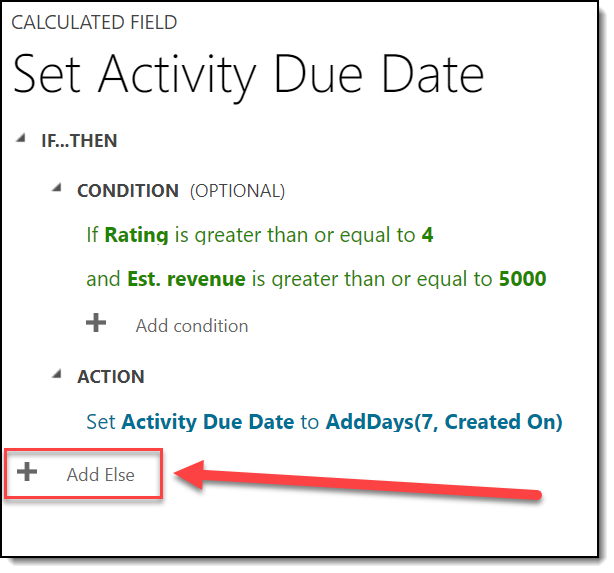
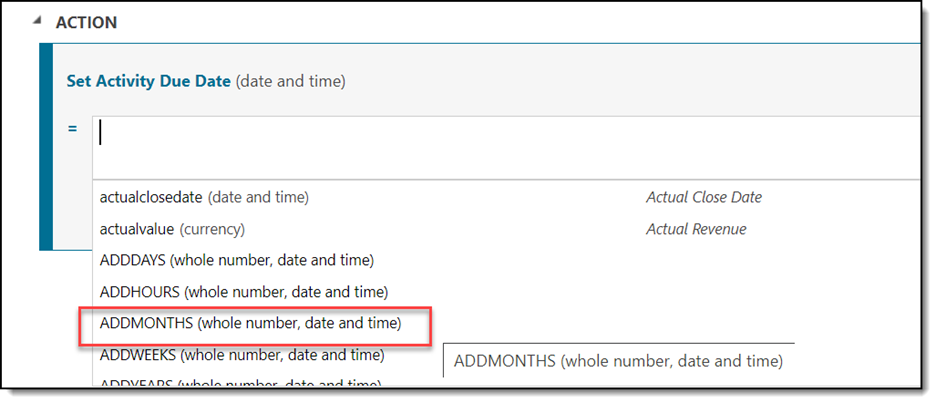
- Since we want to capture ANY other scenario here, we will leave Condition blank. For Action, we will add this:
- The final calculated field builder canvas looks like this:
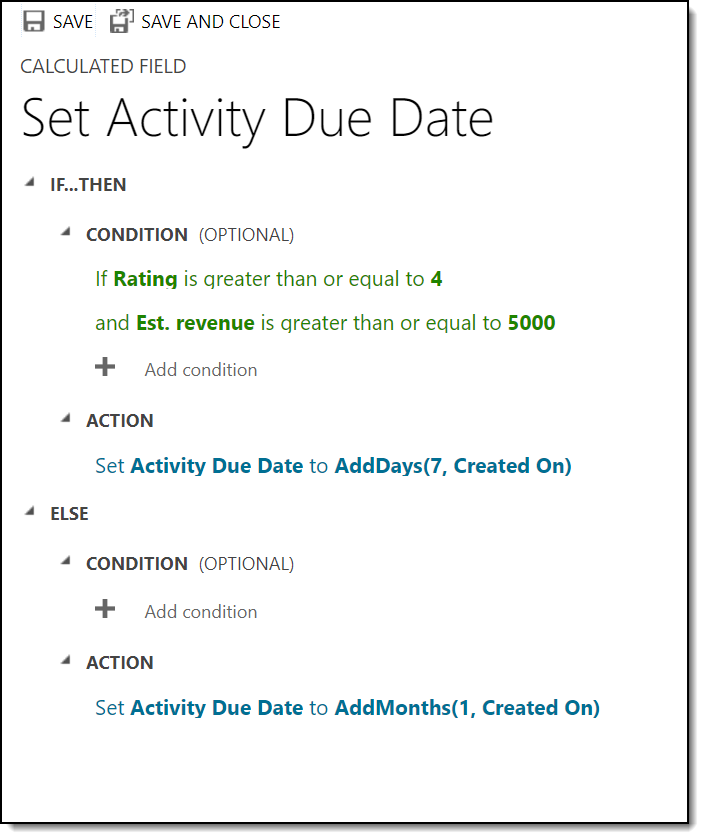
- Click Save and Close at the top.
Calculated Column Limitations
It’s important to note the known limitations of using calculated columns in Dataverse. The full list can be found at this Microsoft Learn article. The important ones are:
- There is a limit of 50 calculated columns per table.
- A calculated column can’t reference itself.
- A calculated column CAN reference other calculated columns.
